Listen to the recording:
#MEAction UK Lay Summary of the 2019 Forward ME Group CBT & GET Survey
Topline findings
A new patient survey of 2274 respondents has confirmed that graded exercise therapy (GET) is harming a large majority of people with ME receiving this treatment in the UK. A majority of people with ME report that cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) led to no change in their physical health; however those who reported a change were more likely to experience deterioration than improvement. More than 3 times as many people reported severe illness after GET than before, and almost 2 times as many reported severe illness after CBT.
Survey background
The preparation and launch of this survey was a collaboration between members of the Forward ME Group, including #MEAction. Its aim was to provide the National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE) with up-to-date data on the experiences of people with ME receiving CBT and GET in the UK since the publication of the 2007 “CFS/ME guideline”. The data will be used to inform the NICE committee as they rewrite the ME guideline.
The survey was made available online between 11th January and 31st January 2019. It was disseminated via the social media channels and email lists of various organisations in the Forward ME Group. To be eligible respondents needed to have a diagnosis of either ME, CFS or PVFS; and to have received or been offered CBT or GET in the UK since 2007. 2274 eligible responses were collected.
- 98.5% reported experiencing post exertional malaise, despite the 2007 NICE guidelines not defining this as a mandatory symptom for diagnosis of ME (NICE, 2007a). Post exertional malaise is, however, now considered a hallmark symptom of ME. (Carruthers et al., 2011, Chu et al., 2018).
- Women accounted for 80.4% of respondents, in line with rates of 75-85% in other studies (Collin et al., 2011, IOM, 2015).
- Responses were received from all age groups, including 184 on behalf of children/young people under the age of 18.
- Most respondents (62.4%) were moderately affected before treatment, whilst 23.8% were mildly affected and 13.8% were severe.
- Over 93% of treatment was offered on the NHS, indicating that treatment was in line with the 2007 NICE guidelines.
- In the majority of responses (53.6%) treatment was started between 1st Jan 2015 and 31st Jan 2019.
Respondents were asked to comment on the impact of CBT or GET. Where they reported being offered both CBT and GET, they were asked to comment on these treatments separately.
Impact of graded exercise therapy
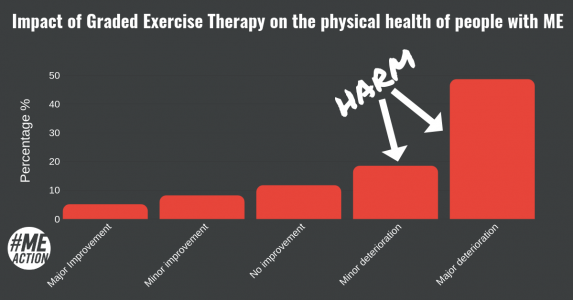
Following treatment, over two thirds (67.1%) of those who underwent GET alone reported deterioration in their physical health. Three quarters (75.4%) of those who underwent GET as well as CBT reported deterioration in physical health, and for the majority (55.9%) this was a major deterioration.
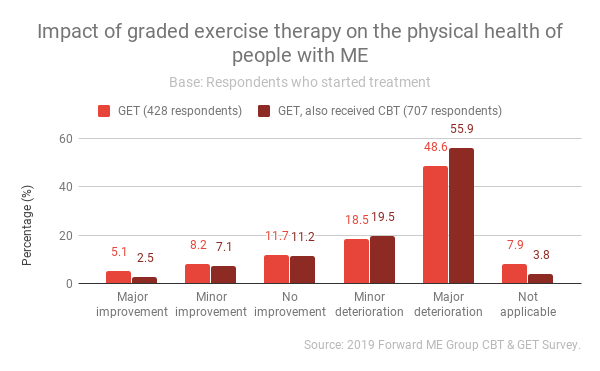
Following roughly the same pattern as impact on physical health, a majority (53%) of those undergoing GET experienced a deterioration in their mental health. This increased to 62.9% when the respondent had also undergone CBT.
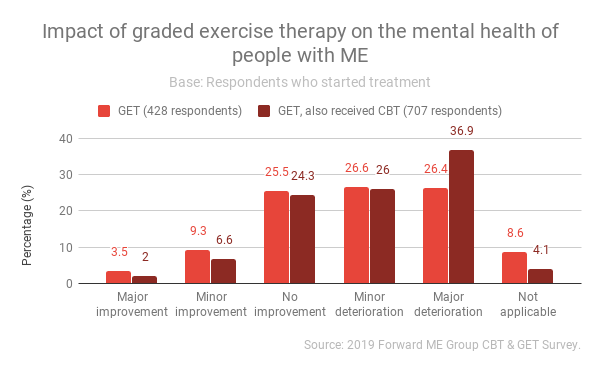
Impact of cognitive behavioural therapy
Most respondents (53%) reported no change in their physical health after CBT. This was also the most common response for those who received GET as well as CBT (48.4%). Whether or not they had received GET as well, more respondents experienced deterioration than improvement in their physical health after CBT.
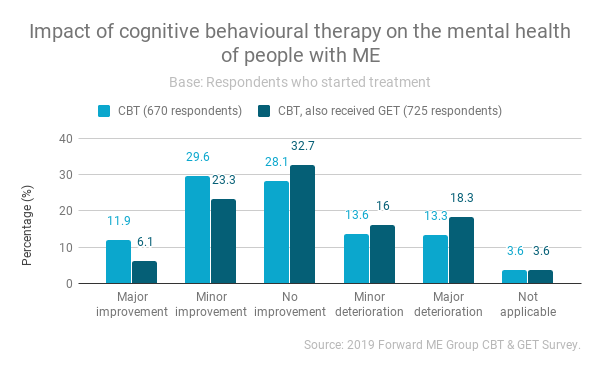
For those who received CBT alone, 41.5% reported an improvement in their mental health whilst 55% reported no change (28.1%) or a deterioration (26.9%). When GET was received as well as CBT, rates of improvement after CBT decreased significantly (26.9%) whereas rates of no change (32.7%) and deterioration (34.6%) increased.
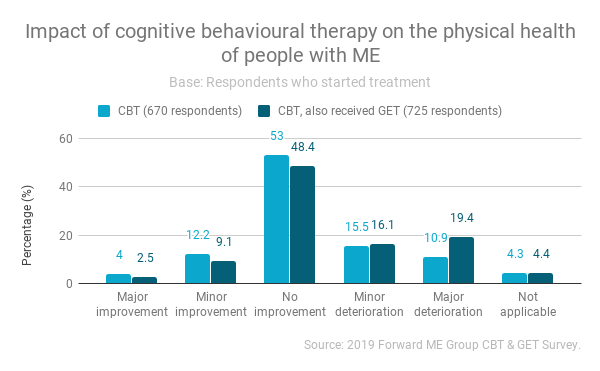
Impact of CBT and GET on symptoms
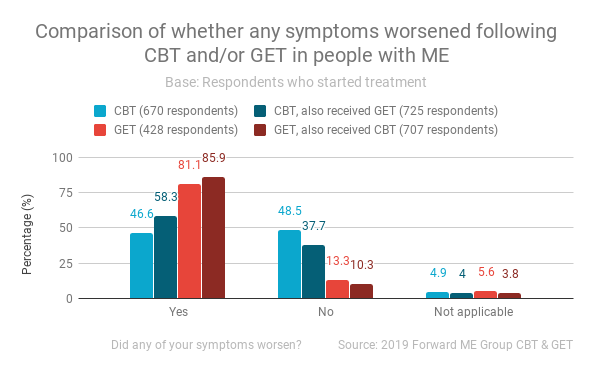
Separately to overall impact on health, respondents were asked if any of their symptoms worsened.
- GET led to a worsening of symptoms for 81.1% of those who received GET alone and 85.9% of those who received both GET and CBT.
- CBT led to a worsening of symptoms for 46.6% of those who received CBT alone and 58.3% of those who received both CBT and GET.
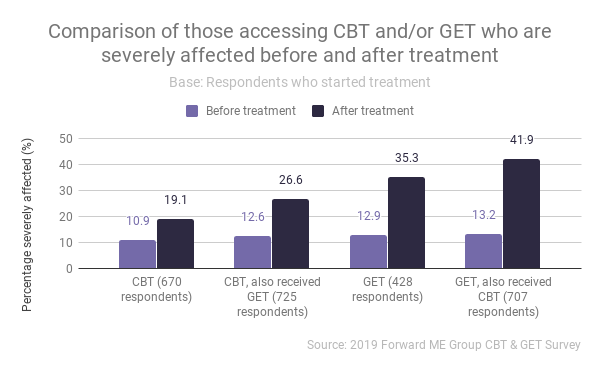
Severe illness
All respondents were asked to report the severity of their illness before treatment and after treatment. The precoded answers of mild, moderate and severe were defined as per the current NICE guidance (NICE, 2007b). Independent of treatment course, more respondents reported being severely affected after treatment than before. The numbers of those reporting severe illness after GET increased by over 3 times in comparison to before. After CBT, almost 2 times as many reported severe illness than before.
Discussion
Overall, the demographics of the sample of respondents appear to be broadly representative of the general population of people with ME. 13.8% reported severe illness against the 2007 NICE definition (NICE, 2007b). However, as this definition differs from those used in previous studies on severity, it’s unknown whether the sample reflects the accepted distribution of 25% of people with ME being housebound and/or bedbound (IOM, 2015, Pendergrast, 2016).
The 2007 NICE guidelines state that “cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) and/or graded exercise therapy (GET) should be offered to people with mild or moderate CFS/ME” and does not recommend these treatments for people with severe ME (NICE 2007c). However, this survey demonstrates that, by their own definitions and against their recommendations, a significant number of people with severe ME are being prescribed CBT and/or GET.
The vast majority reported being offered CBT or GET on the NHS, not privately, implying treatment was in line with the 2007 NICE guidance. This, coupled with a majority reporting starting treatment within the last 4 years, indicates that these results can be taken as an accurate assessment of the impact the 2007 NICE guidelines recommendations of CBT and GET are currently having on people with ME, CFS or PVFS in the UK.
GET is having a negative impact on the physical and mental health of the majority receiving it. CBT, whilst improving the mental health of a significant minority, is leading to no change or a negative impact in terms of both physical and mental health for a majority, with more experiencing deterioration than improvement in their physical health.
Furthermore, when asked if any of their symptoms worsened after treatment a majority responded ‘yes’, suggesting claims that CBT or GET support symptom management, even if they are not curative, should be re-evaluated.
In conclusion, these results clearly show that GET and CBT are not safe treatments for people with ME, CFS or PVFS. For those who received both treatments, reported outcomes are even worse. The results parallel those of previous patient surveys (Geraghty et al., 2016) and reinforce the call for GET and CBT to be suspended as treatments immediately.
Further data from this survey have been analysed by Oxford Brookes University here, and you can find the appendices with the data this report has been written from here.
This summary with references can also be read in PDF format here.





2 thoughts on “GET and CBT are not safe for ME – summary of survey results”
Thank your for the effort you put into this and the valuable insights you give!
A appreciate the appendix in particular. Is the row data available somehow?
After telling my PHP about my personal experiences with GET and CBT therapy, he concluded that it was psychological, and that I should try taking antidepressants even though I was not diagnosed with any form of depression. I promptly changed PHP’s after this. Then my new doctor retired, leaving me with the onerous task of finding a proper PHP that will not only listen to me, but follow the current diagnostic and treatment regimen’s proven protocol(s) to help alleviate my symptomological state especially when faced with post exertional malaise. Time isn’t our friend in this regard. Hopefully people infected with long covid will spur more research into ME/CFS as the numbers increase exponentially over the next few years.
Comments are closed.